Table of Contents:
- What is Zero-Knowledge Proof?
- History of Zero-Knowledge Proof
- Types of Zero-Knowledge Proof
- Working of Zero-Knowledge Proofs
- Zero-Knowledge Applications in Blockchain
- Zero-Knowledge Proofing Techniques
- ZK Rollups (ETH Scaling)
- ZK Based Privacy Protocols
What is Zero-Knowledge Proof?

A zero-knowledge proof is a way of proving if a certain statement is true or not without actually revealing the statement itself. Here, the ‘prover’ is the party trying to prove a claim, while the ‘verifier’ is responsible for validating the claim.
In Simpler Terms, Zero-knowledge proof (ZK proof) technologies enable one party to prove to another party that they know something without actually sharing the information with another party in order to prove their knowledge.
A Use Case:Let's Suppose I want to take a loan, But don’t want to reveal my financial history to banks. Using Zero-Knowledge proof, bank will be able to verify my financial history (e.g. credit score, proof of residence, account payments, and real estate) without knowing any specific data about those assets.
History of Zero Knowledge Proofs?
Zero-knowledge proofs were first devised by MIT researchers Shafi Goldwasser, Silvio Micali, and Charles Rackoff in a 1985 paper, “The Knowledge Complexity of Interactive Proof-Systems”. The paper introduced key concepts including an interactive proof (IP) hierarchy and conceived the concept of knowledge complexity, a measure to see how much proof is transferred from the prover to the verifier.
Perhaps most importantly, they gave the first zero-knowledge proof for a concrete problem when they demonstrated how to construct ZKPs for any NP-set, with any commitment scheme.
Types of Zero Knowledge Proofs?
The two fundamental types of ZKPs include the following:
- Interactive ZeroKnowledge Proofs: In Interactive ZKP, The verifier challenges the prover who provides replies to these challenges until the verifier is convinced. They need to be simultaneously online and the prover must complete a series of actions to convince the verifier about a specific fact.
- Non-Interactive ZeroKnowledge Proofs: Non-interactive Zero-Knowledge Proofs do not require an interactive process between the prover and verifier. The prover delivers the proof to the verifier and the proof can be verified by the verifier only once at any time. It requires more computational power as compared to Interactive Zero Knowledge Proof.
Working of Zero-Knowledge Proof:
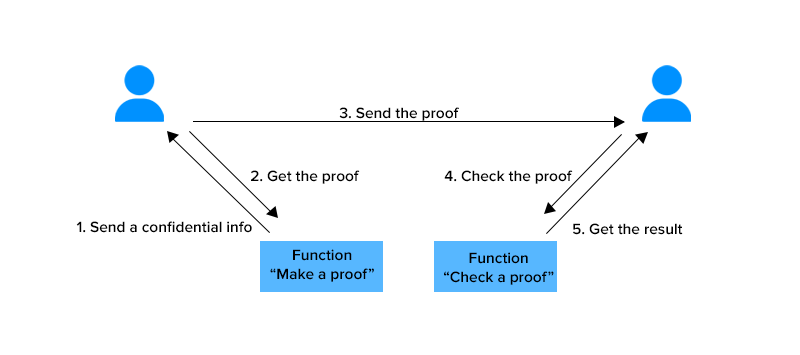
In basic form, a zero-knowledge proof is made up of three elements: witness(confidential Info), challenge, and response.
- Witness: With a zero-knowledge proof, the prover wants to prove knowledge of some hidden information. The secret information is the “witness” to the proof, and the prover’s assumed knowledge of the witness establishes a set of questions that can only be answered by a party with knowledge of the information. Thus, the prover starts the proving process by randomly choosing a question, calculating the answer, and sending it to the verifier.
- Challenge: The verifier randomly picks another question from the set and asks the prover to answer it.
- Response: The prover accepts the question, calculates the answer, and returns it to the verifier. The prover’s response allows the verifier to check if the former really has access to the witness. To ensure the prover isn’t guessing blindly and getting the correct answers by chance, the verifier picks more questions to ask. By repeating this interaction many times, the possibility of the prover faking knowledge of the witness drops significantly until the verifier is satisfied.
The Application of Zero Knowledge Proof in BlockChains?
There are many applications of Zero Knowledge Proof, In this blog, we will be covering applications of ZK in Block Chains:
- Private transactions on blockchains: Transaction data is encrypted and proof posted to prove it was computed correctly. ZKPs are also used in private transactions that do not reveal monetary data and receiver and sender information. An example is Tornado Cash, a decentralized, non-custodial service that allows users to conduct private transactions on Ethereum
- Performance optimizations: Application code is executed off-chain, or by a single node on the blockchain network, and only proof of its correct execution is posted to the blockchain for other parties to verify its correctness. An example is ZK Rollups, where transactions are executed off-chain and finally, a summary of all transactions is then submitted on-chain.
- Transferring private blockchain transactions: The most notable concern in private blockchain transactions is the numerous loopholes evident in conventional procedures. The productive integration of ZKP with private blockchain transactions can create a powerful hacker-proof process.
- Data Security and Privacy: Organizations that control sensitive data, such as banks and hospitals, must keep them free from third-party access. ZKPs and blockchain together can make accessing data impossible.
Zero-knowledge Proofing technologies:
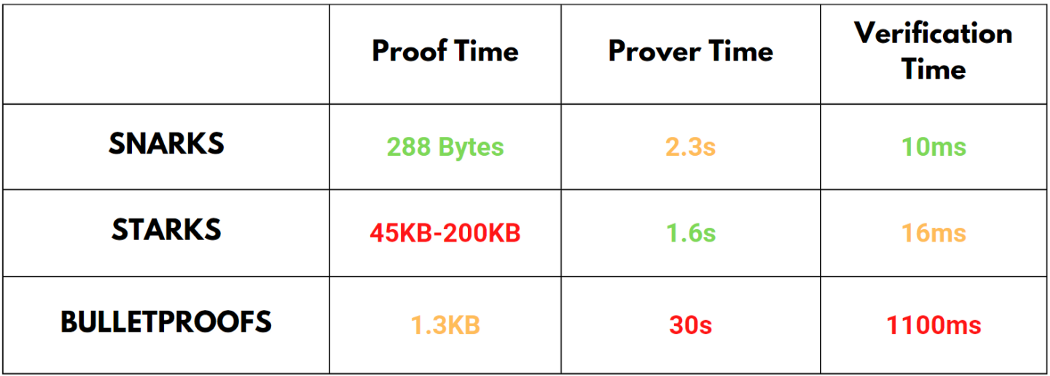
1. zk-SNARK
SNARK stands for “zero-knowledge succinct non-interactive argument on knowledge.” A SNARK is a type of cryptographic proof that is small in size and easy to verify. SNARKs generate a cryptographic proof using elliptical curves, which assume that it’s infeasible to find the discrete logarithm of a random elliptic curve element from a publicly known base point. Computing elliptic curves are less computationally expensive than computing hashing functions used by STARKs, which is why SNARK-based protocols can be more gas efficient.
2. zk-STARKS
STARKS stands for “zero-knowledge scalable transparent argument of knowledge.” It’s a type of cryptographic proof that requires little to no interaction between the prover and the verifier. The key advantages of STARKs over SNARKs are that they have fast prover times and are easier to scale as they offer more computing power. Also, using hash functions makes them quantum resistant.
3. Bulletproofs
Bulletproofs are short, non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs that can convince a verifier that an encrypted value lies within a stated range without disclosing any information about the number.Bulletproofs is a type of range proof that employs zero-knowledge proofing techniques similar to those seen in zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs. Like zkSTARKs, bulletproofs do not require an initial trusted setup ceremony or procedure. Also, they are smaller than zkSTARKs and have significant efficiency and security.
zk-Rollups
Rollups are Layer 2 protocols built on top of Ethereum. Rollups process transactions off-chain, primarily on a rollup-specific chain, and then batch, compress, and deliver the transaction data to the main Ethereum chain. Shifting computation off-chain helps reduce congestion on Ethereum and reduce overall gas costs for users.
ZK Rollups Projects:
zkSync
Loopring
Polygon Hermez
ZK- Based Privacy Protocols
Zero-knowledge proofs power several privacy protocols today due to their non-disclosure feature. With ZK-proofs, users can currently transact on privacy-enabled blockchains and post proofs that confirm that their transactions are valid, and don’t reveal any extra info.
Popular privacy coin, Zcash, uses zk-SNARK cryptography to restore blockchain anonymity for its users and give them control over their transaction information. For instance, when a Zcash user sends coins to another Zcash user, the only available proof of their privacy-enabled transaction comes with zero knowledge. A third-party observer cannot find any additional information about the nature of the transaction, nor the parties and amounts involved.
ZK- Based Privacy Projects:
Zcash
Tornado Cash


All Comments